Xi Jinping Addresses Economic Challenges Ahead: Insights on China’s Stimulus Efforts
Xi Warns of Obstacles Ahead in First Speech After Stimulus Plans
In a recent speech marking the 75th anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China, President Xi Jinping expressed caution regarding the country’s economic outlook. He emphasized the need for vigilance against potential dangers, stating, “We must be mindful of potential dangers and be prepared for rainy days.” This speech marked his first public comments following the announcement of an unprecedented stimulus package aimed at revitalizing the economy amid slowing growth.
While Xi's remarks did not elaborate on specific economic measures, they followed a series of policy announcements that included interest-rate cuts and support for both the housing and stock markets. He warned that “the road ahead cannot be smooth,” acknowledging that “there will be obstacles and difficulties, even major challenges like surging torrents and storms.” These sentiments reflect the current state of China's economy, which is grappling with a prolonged housing slump, weak domestic demand, and falling prices, making the government’s growth target increasingly elusive.
Recent Economic Data and Market Response
The context for Xi's comments is troubling: Chinese consumer confidence fell in August to its lowest level since November 2022, and figures released earlier indicated that industrial activity contracted for the fifth consecutive month in September. The pessimism surrounding the economy was palpable before the stimulus measures were announced. However, these announcements have had a positive immediate impact on the stock market, with Chinese equities experiencing their largest weekly rally since 2008, gaining over 20% since the previous Monday, thus entering a technical bull market.
Despite these positive signs in the market, analysts and economists are concerned about the effectiveness of the government’s measures. China’s economy remains fragile, with significant challenges such as weak domestic demand and corporate reluctance to borrow.
Weak Domestic Demand: A Persistent Challenge
At the heart of China's economic struggles lies the persistent issue of weak domestic demand. Chinese consumers, who tend to prioritize savings—accounting for around 35% of the nation’s GDP compared to about 15% in the U.S.—have shown slow recovery in consumer confidence. This cautious spending behavior has led to a decline in economic activity, particularly impacting sectors like manufacturing and services.
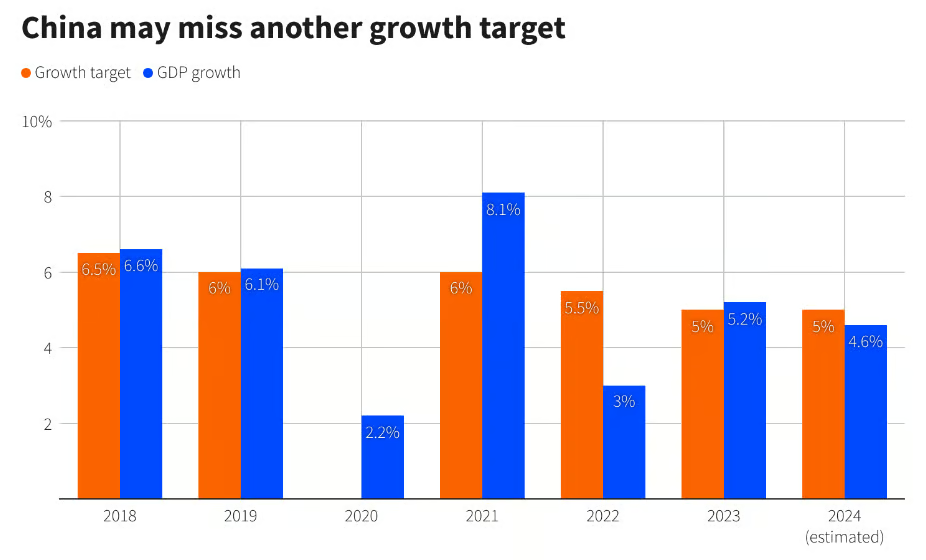
Furthermore, corporate demand for loans has hit a 14-year low, casting doubt on the sustainability of any recovery efforts. Without an uptick in consumer spending and corporate investment, even aggressive stimulus measures may fall short of achieving the government's ambitious growth target of 5% for the year.
Boosting Markets: A Fragile Solution?
The Chinese stock market has also faced significant declines, with its market capitalization shrinking from $16.5 trillion in 2021 to approximately $12 trillion. In an effort to stabilize the market, the government has injected 500 billion yuan into the financial system to enhance liquidity for brokers, insurers, and financial institutions. Additionally, 300 billion yuan has been earmarked for stock buybacks and acquisitions.
While these initiatives might provide a temporary market boost, they represent less than 1% of the total market value, leaving investors cautious. The broader economic structural issues continue to loom large, raising doubts about whether short-term measures will be enough to reverse the ongoing contraction.
Targeted Stimulus to Propel New Growth Sectors
Despite these obstacles, China is shifting its focus toward more sustainable growth sectors such as advanced manufacturing, climate change initiatives, and renewable energy. Former People’s Bank of China Deputy Governor Zhu Min highlighted that the stimulus package, while modest, is designed to be precisely targeted. The aim is to channel resources into sectors deemed future growth drivers rather than relying on traditional economic engines like the property market and infrastructure.
This targeted approach is intended to avoid exacerbating China's high debt levels, which currently stand around 280% of GDP. The recent measures represent part of a broader strategy to address structural issues instead of implementing large-scale, indiscriminate funding.
Easing Lending and Financial Cushioning
In conjunction with fiscal measures, the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) has initiated monetary easing to facilitate lending. Key moves include cutting the reserve requirement ratio (RRR) by 50 to 100 basis points to enhance liquidity for banks and reducing the loan prime rate (LPR) by 20 to 25 basis points, thereby lowering borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. This is expected to stimulate borrowing and investment.
Additionally, the PBoC plans to inject 1 trillion yuan into state banks through sovereign bond issuance, aimed at bolstering the financial system’s resilience against external shocks. The objective is to enhance liquidity and provide institutions with the necessary resources to absorb potential losses.
However, while these monetary moves may offer short-term relief, questions persist regarding their ability to foster sustained economic growth amid broader global uncertainties.
Property Market Stagnation
China's property market continues to face significant challenges, including declining land sales and ongoing debt issues. The PBoC has encouraged banks to reduce mortgage rates and ease down payment requirements for second-home buyers in an attempt to provide some relief. Nevertheless, the property sector remains a significant drag on the economy, and Zhu Min has warned against large-scale stimulus directed at real estate due to China’s high debt levels.
Modest Fiscal Measures and Economic Uncertainty
On the fiscal front, the Chinese government has announced relief measures totaling 154 billion yuan, primarily focused on poverty alleviation and disaster relief. However, these initiatives appear minimal compared to China's annual household consumption of 47 trillion yuan, leading critics to question their potential impact on boosting consumption amidst persistently low consumer confidence.
Concerns regarding local government debt are also rising, particularly as borrowing increases for financing platforms. Vice Finance Minister Zhu Zhongming has sought to assuage these fears, stating that government debt risks remain “manageable.”
Economic Growth Outlook: Stabilization in Sight?
Despite the ongoing challenges, Zhu Min maintains a cautiously optimistic outlook, expecting the economy to expand by around 5% this year, with growth in 2024 likely to range between 4.5% and 5%. This forecast aligns with the predictions of economists polled by Bloomberg, who share similar growth expectations.
Recent data from the third quarter suggests that the Chinese economy may be stabilizing, even as the property sector continues to pose challenges. While the situation remains precarious, indicators of recovery are emerging.
Global Impact and Investor Sentiment
The global community is closely monitoring the implications of China’s stimulus measures, as the country's economic health plays a crucial role in the global economy. While targeted measures may provide temporary relief, investor sentiment remains cautious due to long-term risks tied to structural challenges. Although emerging sectors like advanced manufacturing and renewable energy could see growth, uncertainties surrounding debt levels and property market weaknesses continue to exert pressure.
For global investors, these risks may enhance the appeal of safe-haven assets like gold. As uncertainties persist and the potential for slower-than-expected recovery looms, market strategies may shift toward more defensive positions to hedge against volatility.

Conclusion: A Balancing Act for Sustainable Growth
China’s recent stimulus package represents a strategic shift, targeting sectors with potential for future growth while seeking to manage existing debt challenges. However, achieving a sustainable recovery will depend on addressing underlying structural issues such as weak consumer confidence, high debt levels, and a troubled property market.
While the recent measures may help stabilize the economy in the short term, their long-term effectiveness remains uncertain. Comprehensive reforms may be necessary for China to sustain economic growth and remain competitive on a global scale. Investors are advised to approach the situation with caution, remaining vigilant to the evolving dynamics as China navigates these significant challenges.

Shaun
Founder
With over a decade of expertise spanning investment advisory, investment banking analysis, oil trading, and financial advisory roles, RealisedGains is committed to empowering retail investors to achieve lasting financial well-being. By delivering meticulously curated investment insights and educational programs, RealisedGains equips individuals with the knowledge and tools to make sophisticated, informed financial decisions.
The Easiest Way Ever To Pass Your Financial Licensing Exam With Minimum Time And Money
Your career deserves the best tool
Disclaimer: Practice materials are 100% original by RealisedGains — unaffiliated with IBF, SCI, or MAS, for educational use only.
With over a decade of expertise spanning investment advisory, investment banking analysis, oil trading, and financial advisory roles, RealisedGains is committed to empowering retail investors to achieve lasting financial well-being. By delivering meticulously curated investment insights and educational programs, RealisedGains equips individuals with the knowledge and tools to make sophisticated, informed financial decisions.
© 2025 RealisedGains | All Rights Reserved | www.realisedgains.com
The go to platform that keeps you informed on the financial markets. Best of all, it's free.
RealisedGains
The go to platform that keeps you informed on the financial markets. Best of all, it's free.
About
Products
Tools
Market News
Personal Finance
Socials
© 2025 RealisedGains | All Rights Reserved | www.realisedgains.com


