Federal Reserve’s Balance Sheet Reduction
Implications for Financial Markets
The Federal Reserve's ongoing effort to normalize monetary policy through quantitative tightening (QT) has led to a significant reduction in its balance sheet, with bank reserves shrinking by approximately $326 billion to $2.89 trillion as of January 1, 2025. This marks the lowest level since October 2020, signaling a deliberate contraction in liquidity within the banking system. QT, initiated in June 2022, involves allowing maturing securities to roll off without reinvestment, reducing the Fed's asset holdings and tightening monetary conditions. This reduction aims to temper inflationary pressures by curbing excess liquidity, but its consequences on financial stability are a growing concern as reserves approach critically low levels.
The mechanics of this balance sheet reduction are pivotal to understanding its broader impact. By not reinvesting the proceeds of maturing securities, the Fed effectively decreases the reserves held by commercial banks, forcing them to seek alternative funding sources. Additionally, the central bank adjusts the interest rate on its overnight reverse repurchase (RRP) facility, which serves as a tool to manage short-term interest rates and system-wide liquidity. These combined measures create a more restrictive monetary environment, influencing borrowing costs and investment behaviors. However, this strategy comes with risks, particularly as reserves near thresholds that could destabilize short-term funding markets.
The Role of Seasonal Dynamics in Reserves Decline
Beyond the structured effects of QT, year-end dynamics contribute to the sharp fluctuations in reserves. Financial institutions routinely adjust their balance sheets at the close of the year to meet regulatory requirements, often reducing activities like repurchase agreements. This seasonal behavior temporarily reduces available liquidity, compelling a higher utilization of the Fed’s RRP facility, which absorbs excess funds from the financial system. For instance, balances in the RRP facility surged by $375 billion in late December 2024 before retracting by $234 billion in early January 2025. These fluctuations reflect temporary adjustments but can exacerbate liquidity strains, especially when combined with the structural effects of QT.
The interaction between seasonal dynamics and structural QT policies creates a complex landscape for liquidity management. While year-end reductions in market activity are expected to normalize, they underscore the vulnerability of the system to sudden reserve declines. For financial markets, such fluctuations can lead to unpredictable shifts in short-term interest rates, increasing borrowing costs for banks and businesses. Policymakers must remain vigilant to ensure that seasonal liquidity demands do not collide with broader QT-induced constraints, which could amplify volatility and stress in financial markets.
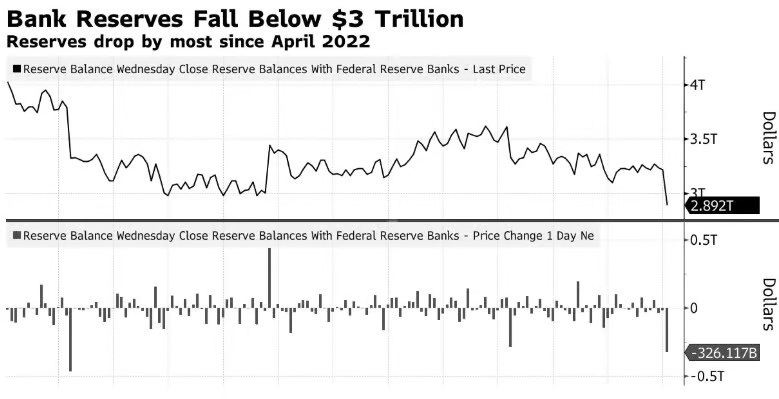
Market Implications and Historical Comparisons
The current contraction in reserves raises parallels to the liquidity crunch of September 2019, when a sudden shortage of reserves caused short-term lending rates to spike sharply. During that episode, the Federal Reserve intervened with emergency measures to stabilize markets, highlighting the risks of allowing reserves to fall too low. Today, analysts estimate that a “comfortable” reserve level would range between $3 trillion and $3.25 trillion, including a safety buffer. The recent dip below this range raises concerns about potential market instability if reserves continue to shrink unchecked.
Historical precedent suggests that the Federal Reserve must carefully balance its QT efforts with the need to maintain adequate reserves to prevent market disruptions. The Fed’s close monitoring of liquidity conditions will likely determine the pace of QT moving forward. A repeat of the 2019 scenario could undermine confidence in the Fed’s ability to manage monetary policy effectively, potentially triggering broader financial market volatility. This highlights the importance of proactive interventions to ensure smooth market functioning while pursuing balance sheet normalization goals.
Projections for QT’s Conclusion
Market expectations for the end of QT are increasingly coalescing around the first half of 2025. Surveys from the New York Fed’s Open Market Desk reveal that most respondents anticipate QT will conclude within this timeframe, as reserves approach levels that could jeopardize system stability. Current projections estimate that continued balance sheet runoff will bring reserves to around $2.5 to $3 trillion by mid-2025, a range that may prompt the Fed to halt the process to prevent liquidity shortfalls.
These expectations align with the view that quantitative tightening, while necessary to combat inflation, cannot persist indefinitely without risking significant disruptions in funding markets. As reserves approach critical thresholds, the Fed faces a delicate balancing act. Halting QT too early could undermine its inflation-fighting credibility, while persisting for too long risks unintended tightening of financial conditions, particularly in sectors reliant on short-term financing. Striking the right balance will be crucial to maintaining economic stability and market confidence.
Debt Ceiling Constraints and Liquidity Challenges
Complicating the Fed’s QT strategy is the reinstatement of the U.S. debt ceiling, which adds another layer of uncertainty to liquidity management. When the Treasury operates under the debt cap, it often employs extraordinary measures that can temporarily inject or drain liquidity from the financial system. These actions, while necessary to navigate fiscal constraints, create additional challenges for the Fed in gauging the true availability of reserves and adjusting its policy stance accordingly.
The interplay between fiscal and monetary policy during periods of debt ceiling constraints underscores the complexity of managing liquidity in the current environment. For markets, this uncertainty translates into heightened volatility and risk premiums, particularly in short-term funding instruments like Treasury bills and repurchase agreements. The Fed’s ability to effectively coordinate with fiscal authorities will be critical in minimizing disruptions and maintaining confidence in U.S. financial markets.
Broader Implications for Financial Markets
The ongoing reduction in bank reserves and balance sheet normalization has profound implications for financial markets. By tightening liquidity conditions, the Fed’s QT program influences asset prices, borrowing costs, and overall market sentiment. A shrinking balance sheet raises the cost of capital, potentially slowing economic growth and impacting sectors reliant on cheap financing. At the same time, the risk of funding market volatility looms large, particularly as reserves approach critically low levels.
For investors, the current environment necessitates caution and a renewed focus on liquidity risk. The interplay between monetary tightening, fiscal constraints, and seasonal dynamics creates a complex backdrop for decision-making. While the Fed’s actions aim to ensure long-term economic stability, their near-term effects on financial markets underscore the challenges of managing such a multifaceted transition. The coming months will be critical in determining how effectively the Fed can balance its dual mandates of price stability and financial stability.

Shaun
Founder
With over a decade of expertise spanning investment advisory, investment banking analysis, oil trading, and financial advisory roles, RealisedGains is committed to empowering retail investors to achieve lasting financial well-being. By delivering meticulously curated investment insights and educational programs, RealisedGains equips individuals with the knowledge and tools to make sophisticated, informed financial decisions.
The Easiest Way Ever To Pass Your Financial Licensing Exam With Minimum Time And Money
Your career deserves the best tool
Disclaimer: Practice materials are 100% original by RealisedGains — unaffiliated with IBF, SCI, or MAS, for educational use only.

Founder, Analyst
With over a decade of expertise spanning investment advisory, investment banking analysis, oil trading, and financial advisory roles, RealisedGains is committed to empowering retail investors to achieve lasting financial well-being. By delivering meticulously curated investment insights and educational programs, RealisedGains equips individuals with the knowledge and tools to make sophisticated, informed financial decisions.
© 2025 RealisedGains | All Rights Reserved | www.realisedgains.com
The go to platform that keeps you informed on the financial markets. Best of all, it's free.
RealisedGains
The go to platform that keeps you informed on the financial markets. Best of all, it's free.
About
Products
Tools
Market News
Personal Finance
Socials
© 2025 RealisedGains | All Rights Reserved | www.realisedgains.com

